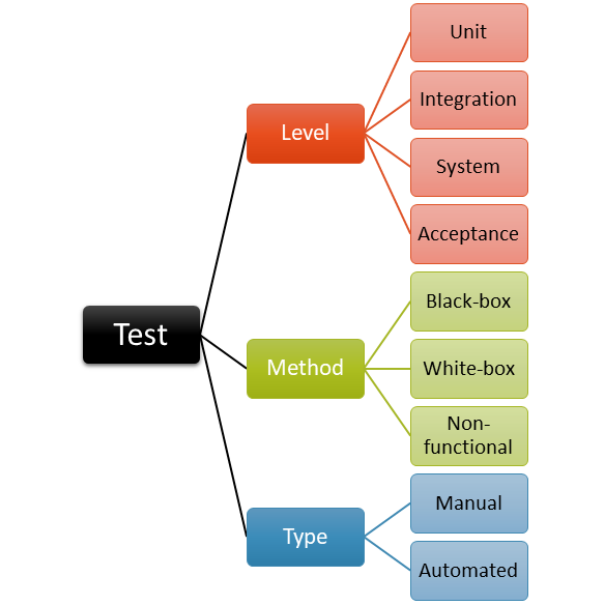
The Importance of Functional Testing in Software Development
Functional testing
is a crucial process in software development, involving four primary forms: unit testing, white box testing, gorilla testing, integration testing, and gray box testing.
Understanding End to End Testing
End to End testing
involves testing an entire application environment in a real-world usage condition, such as connecting with a database, leveraging network connections, or integrating with other hardware, programs, or systems.
Importance of Smoke Testing
Smoke testing
ensures that fundamental and crucial functionality of the system is operating correctly at a high level. Acknowledging the importance of acceptance testing is crucial in ensuring the successful implementation of an application.
Acceptance Testing for Successful Implementation
Acceptance testing
, ensures that their applications meet the necessary requirements and maintain user satisfaction. Acceptance testing is a crucial step in software development, where the software is tested in real-time business scenarios before being released to the market. This process is known as User Acceptance Testing (UAT).
Exploring Non-Functional Testing
Non-functional testing
includes security testing, penetration testing, and performance testing. Performance testing is a crucial aspect of software development, assessing an application’s stability and reaction time by introducing load.
Diverse Forms of Load Testing
Load testing
involves adding a load equivalent to or fewer than the planned number of users to test the application’s response time. Stress testing assesses the application’s stability and reaction time by introducing load higher than the expected number of users.
Evaluating Usability and Accessibility
Endurance testing
(Soak Testing) evaluates the application’s stability and reaction time by applying load constantly for a longer duration. Usability testing evaluates a program from the user’s perspective to assess its appearance, feel, and user-friendliness.
Additional Testing Techniques
Exploratory testing
is informal testing conducted by the testing team to explore the application and identify faults. Cross-browser testing involves testing a program on multiple browsers, operating systems, and mobile devices to check look and feel and performance.
Accessibility testing
determines if the software or program is accessible for impaired persons. Other types of testing include system integration testing, system testing, and system verification testing
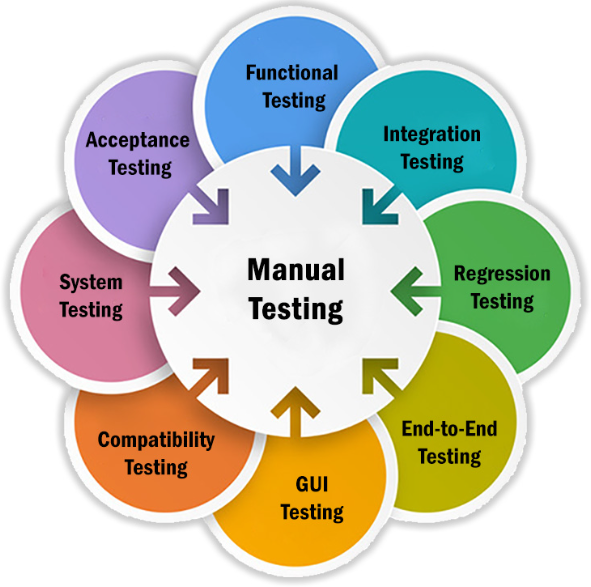
Comprehensive Testing Methods
Each type of testing is essential for ensuring the application’s functionality and usability.
Ad-hoc testing
is an informal method of detecting bugs in an application without a specific test case or documentation.
Back-end testing
involves testing the database structure, schema, stored procedure, and data structure of input or data entered on the front-end application. Browser compatibility testing ensures that web applications work with various browsers and operating systems.
Delving into White Box Testing and Beyond
Boundary value testing
evaluates the behavior of the application at the boundary level, verifying faults at distinct integer values. White box testing is conducted at the unit test level to ensure that each potential route from the decision point is completed at least once for 100% of test coverage.
Comparison Testing
is a method used to compare a product’s strengths and flaws with its earlier versions or similar items. Equivalence Partitioning testing reduces duplicate test cases within a given group, producing the same result but without any flaw.
Experience-based testing
relies on the tester’s knowledge of how the application has operated in the past. Example Testing is real-time testing, which involves real-time situations and scenarios based on the tester’s experience. It also verifies the menu of the application.
Dynamic Testing Approaches
Incremental Integration Testing
is a bottom-up technique for testing an application as new functionality is introduced. It requires the application functionality and components to be independent enough to test individually.
Installation and Uninstallation Testing
is conducted to confirm that the software program is installed successfully and operating as expected. Mutation Testing is a white box testing where the source code of one program is updated and validates whether the current test cases can find problems in the system.
Recovery Testing
examines how effectively the application or system recovers from crashes or catastrophes. Regression Testing involves testing unmodified features of the program to ensure that bug fixes, adding new features, removing, or changing existing features do not harm the functioning application.
Implementing Risk-Based Testing (RBT)
Risk-Based Testing (RBT)
tests capabilities or requirements based on their priority, with high priority features being tested first, followed by medium and low priority functionalities. This strategy is carried out when there is inadequate time available to test the full software and the software must be deployed on time without delay.