Importance of Test Planning
A properly designed test strategy has various benefits:
Aligns testing scope and goals with requirements
Estimates testing effort and resource demands
Identifies testing risks to reduce
Structures test coverage by type and priority.
Serves as a reference for execution and reporting.
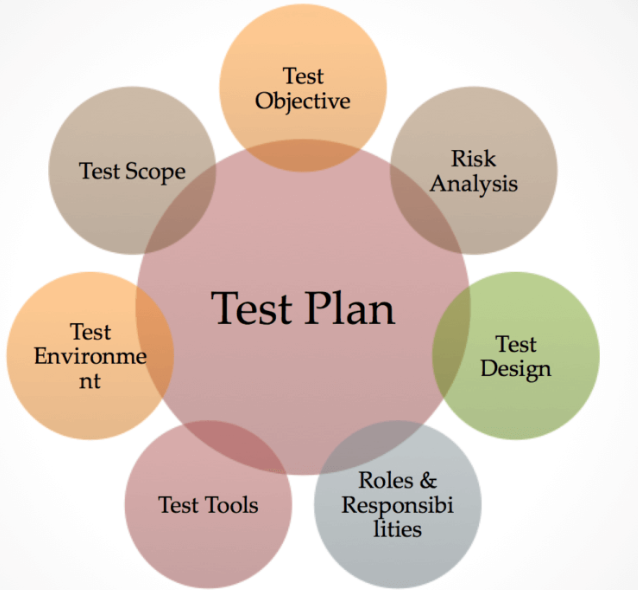
Elements of a Test Plan
Key parts of a test plan document:
Introduction
Background, scope, and aims Requirements Coverage
Traceability matrix connecting requirements to test cases Risk Assessment
Major hazards and mitigating methods Test Coverage
Types of tests to conduct Schedules and Estimates
Timeline, test cycles, effort, resources, and responsibilities
Equipment, employees, and roles Processes
Entry and exit criteria, approvals, and tools
Defining Scope and Objectives
The test plan should define:
Scope : Features, components, and platforms to be tested
Objectives: Goals of testing for the release, quality criteria
Acceptance Criteria: Requirements for approval Clearly defined scope and goals concentrate efforts.
Selecting test approaches
Factors that impact the testing approach:
Risk Business: Criticality, Complexity
Requirements: functional, nonfunctional
Quality Attributes: Security, Performance, Dependability
Resources: time, funding, employee skills
Common testing types:
Unit Testing: Validating modular code units
Integration Testing Testing interfaces between components
System Testing: End-to-end flows across the whole system
Regression Testing: Existing functionality after modifications
Exploratory Testing: Freely researching software behavior
Other sorts, including usability, performance, and security testing

Estimating Testing Effort
Techniques for evaluating test efforts:
Expert Judgment: Leverage experience from earlier projects and team skills.
Metrics: Use historical defect data to draw conclusions.
Test Point Analysis: Assign points to requirements and estimate based on previous productivity.
Test Documentation
A brief summary of documents to define in test planning:
Test Cases: Steps to Test a Requirement
Test data inputs, preconditions, and anticipated outcomes
Test Scripts Automated scripts for regression testing
Test Reports: Track execution progress and results
Alignment with Stakeholders
Key factors for synchronizing test planning throughout the team:
Review scope and priorities with product managers.
Coordinate milestones with development.
Get signoff from leadership on the final plan.
Role of Test Automation:
Issues to consider with test automation:
Identify automation prospects during planning.
Estimate the automation development effort.
Factor in automated maintenance time
Balance manual and automated testing.
Maintaining the Test Plan:
Key considerations for keeping the test plan updated:
Treat it as a live document, review it, and update it periodically.
Share the latest version with all stakeholders.
Use to monitor progress, hazards, and modify scope or priority
Conduct test plan review sessions.
Update traceability between requirements and test cases.